VIP Peptide
$150.00
99% Purity

3rd Party Tested

USA Made
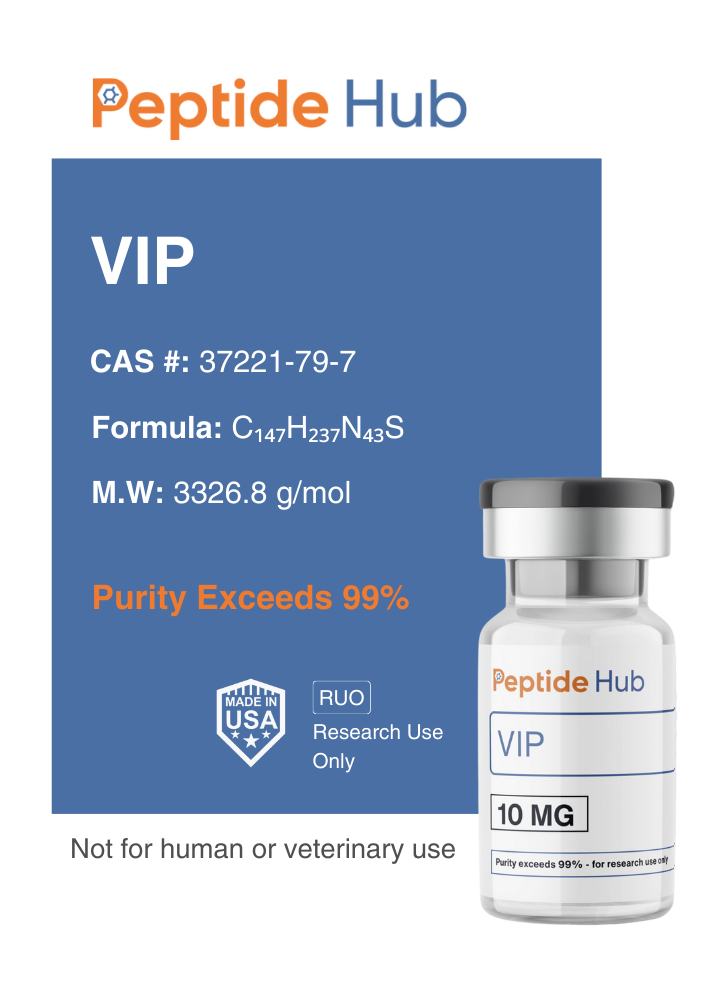
VIP (Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide)
Potential Research Applications
VIP is being researched for its role in:
- Vasodilation and Blood Flow Regulation: VIP is investigated for its potential to induce vasodilation, improving blood flow and reducing vascular resistance, which could have implications for cardiovascular health.
- Digestive Health: VIP is studied for its role in regulating water and electrolyte secretion in the intestines, contributing to proper digestive function and fluid balance.
- Immune System Modulation: VIP is being explored for its potential to modulate immune responses, particularly in conditions of chronic inflammation or autoimmune disorders.
- Neuroprotective Properties: Research is underway to explore VIP’s neuroprotective potential, particularly in neurodegenerative diseases, where inflammation and immune dysregulation play a role.
- Smooth Muscle Relaxation: VIP is being studied for its ability to relax smooth muscle, which could have applications in conditions like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
✔ High-Quality Research Peptides – Produced under stringent quality control standards.
✔ Lab-Tested for Purity – Ensures consistency for scientific studies.
✔ Research Use Only – Not for human consumption or medical applications.
✔ Peptides – Will arrive in a lyophilized (powder) form for maximum stability and ease of reconstitution.
The peptides are available for research and laboratory purposes only. Please review and ahere to our Terms and Conditions before ordering.
- Description
- Certificate of Analysis
VIP (Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide) is a neuropeptide that regulates multiple physiological processes, including circulation, digestion, immune function, and metabolism.
In the gastrointestinal tract, it widens blood vessels, improves blood flow, and lowers blood pressure. Additionally, it relaxes smooth muscles, enhances gastrointestinal motility, and controls fluid and electrolyte secretion. These effects support digestion and overall gut health.
In the central nervous system, VIP influences circadian rhythms, cognitive function, and mood. It also protects neurons by promoting survival and regeneration, making it a key focus in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s research. Moreover, it enhances neurotransmitter release, supporting brain function and mental clarity.
Furthermore, VIP plays a critical role in immune regulation. It reduces inflammatory activity by modulating immune cell responses, helping to prevent excessive inflammation and tissue damage. Researchers explore its potential in treating autoimmune and chronic inflammatory diseases.
In addition, VIP impacts metabolism by influencing insulin secretion and glucose regulation. It helps improve insulin sensitivity, making it an important subject in diabetes research. Its ability to balance metabolic function may also aid in weight management and energy regulation.
Although promising, VIP requires further study to fully understand its effects and therapeutic potential. Researchers continue to investigate its diverse biological roles, aiming to unlock new applications in medicine and biotechnology.
For Research Use Only
No Certificate of Analysis images available for this product.