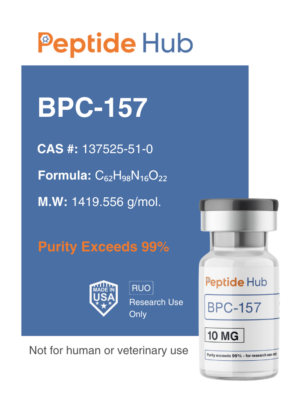
Semaglutide (GLP-1 Analogue) – 5mg
$100.00
99% Purity

3rd Party Tested

USA Made
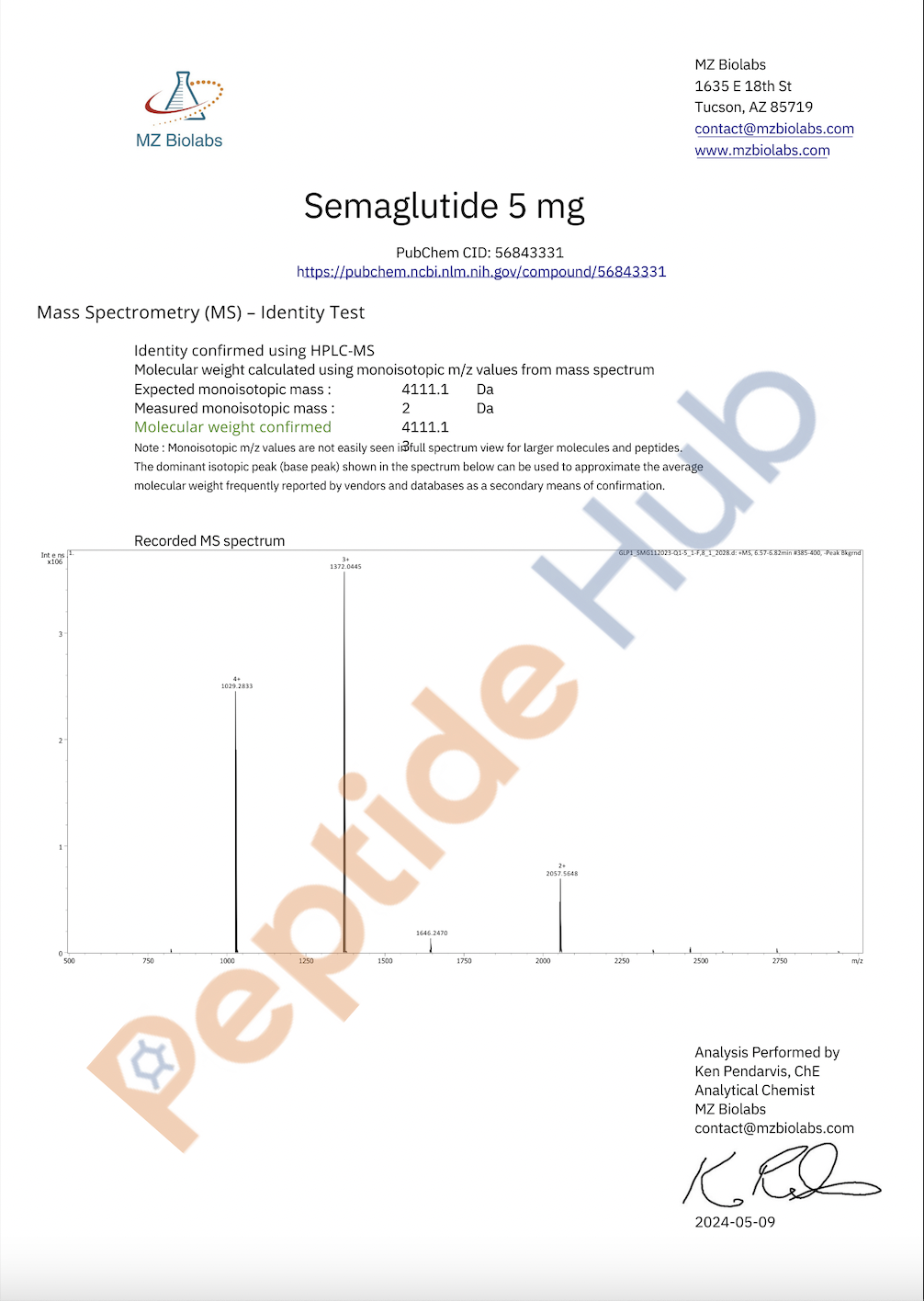
Semaglutide 5mg
Semaglutide 5mg is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist being researched for its role in metabolic function. It is of particular interest in studies related to glucose metabolism, appetite regulation, and potential weight management applications. Semaglutide has been investigated for its effects on insulin sensitivity, glycemic control, and its ability to influence satiety by interacting with GLP-1 receptors.
Potential Research Applications
Semaglutide is currently being studied for its role in:
- Glucose Metabolism: Examined for its impact on insulin secretion and glucose regulation.
- Appetite Regulation: Investigated for its potential role in reducing food intake and influencing satiety signals.
- Weight Management Studies: Researched for its effects on body weight regulation and fat metabolism.
- Cardiovascular Research: Explored for potential benefits in cardiovascular function and inflammation regulation.
✔ High-Quality Research Peptides – Produced under stringent quality control standards.
✔ Lab-Tested for Purity – Ensures consistency for scientific studies.
✔ Research Use Only – Not for human consumption or medical applications.
✔ Peptides – Will arrive in a lyophilized (powder) form for maximum stability and ease of reconstitution.
The peptides are available for research and laboratory purposes only. Please review and ahere to our Terms and Conditions before ordering.
- Description
- Certificate of Analysis
Semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, plays a key role in glycemic control and metabolic regulation. As a synthetic GLP-1 analog, it has a prolonged half-life due to structural modifications. These changes enhance albumin binding and increase resistance to enzymatic degradation. As a result, Semaglutide supports glucose homeostasis and appetite regulation.
Studies show that Semaglutide stimulates insulin secretion in a glucose-dependent manner and suppresses glucagon release. This dual action improves postprandial glucose levels and enhances glycemic control. Additionally, it slows gastric emptying, reducing rapid blood glucose fluctuations. These effects make Semaglutide a strong candidate for treating insulin resistance and dysglycemia in research studies.
Beyond glucose metabolism, Semaglutide also influences weight regulation by suppressing appetite through central mechanisms. GLP-1 receptor activation in the hypothalamus reduces energy intake, leading to significant weight loss.
Researchers continue to explore Semaglutide’s broader benefits, including cardioprotective and neuroprotective effects. Early data suggest it reduces inflammation and improves lipid metabolism. As studies progress, researchers aim to clarify its long-term safety and expand its research applications.