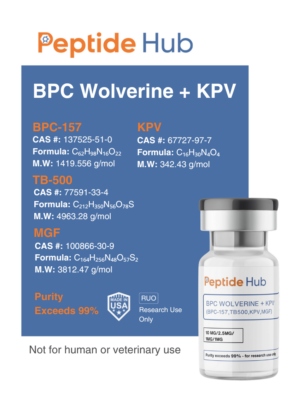
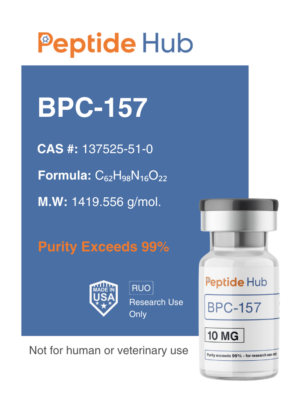
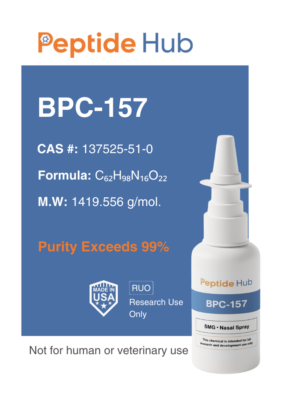
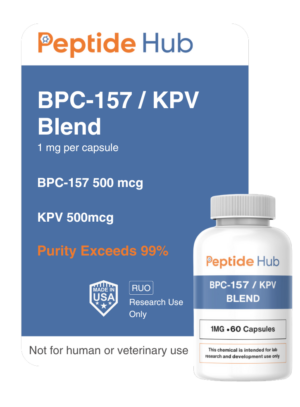
The peptides are available for research and laboratory purposes only. Please review and ahere to our Terms and Conditions before ordering.
- Description
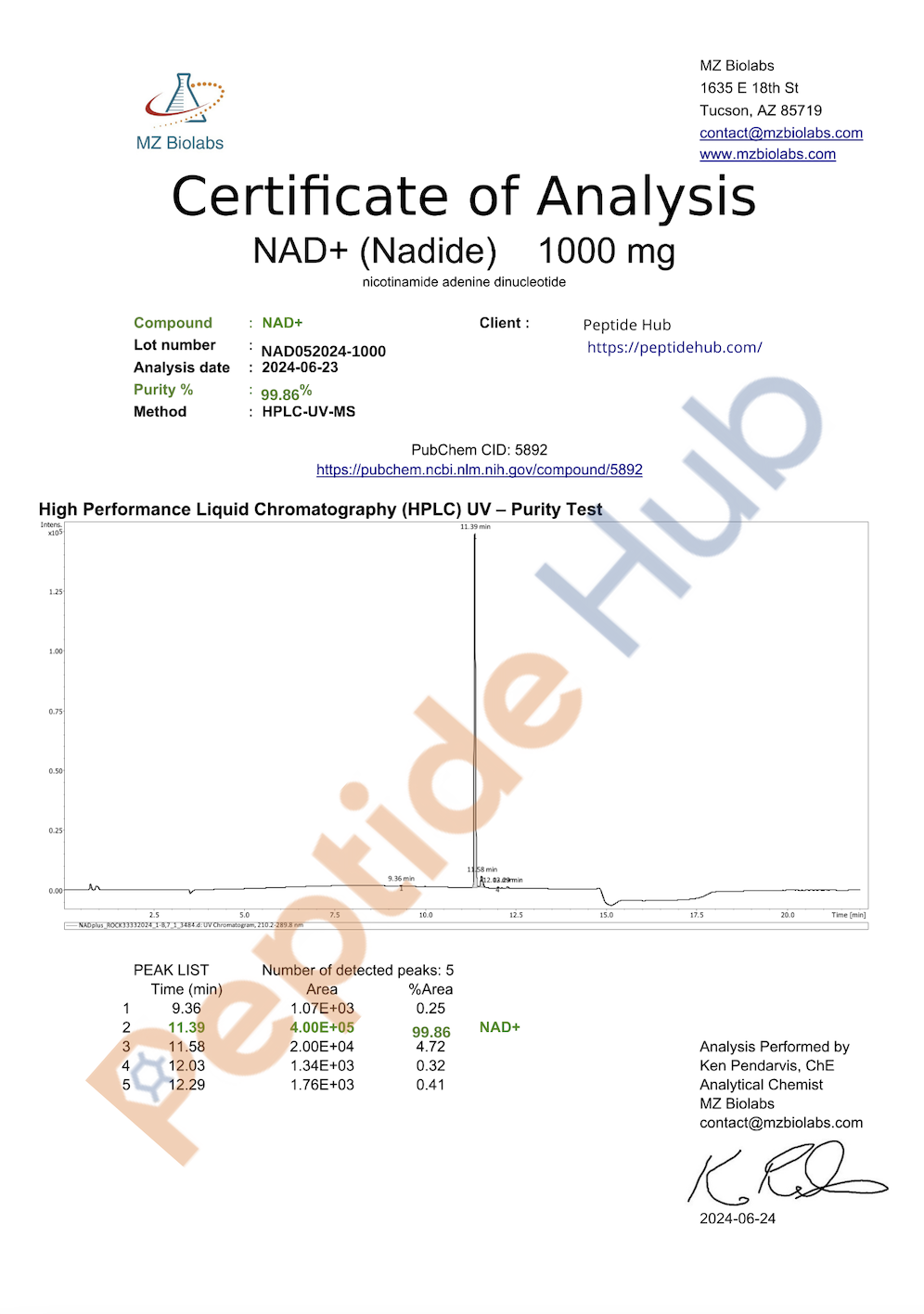
- Certificate of Analysis
NAD+ – 1000mg is a coenzyme essential for cellular energy production and metabolic regulation. Researchers study NAD+ to understand its role in supporting mitochondrial function, enhancing ATP production, and maintaining overall metabolic health. Additionally, NAD+ plays a key role in DNA repair, making it crucial for studies on aging and cell regeneration.
Scientists investigate how it drives metabolic processes by activating enzymes such as sirtuins and PARPs (poly ADP-ribose polymerases). Moreover, they analyze its ability to promote mitochondrial efficiency, which helps sustain energy levels and protect cells from oxidative damage. These studies provide insights into how NAD+ influences longevity and cellular resilience.
Furthermore, researchers examine NAD+'s impact on metabolic disorders, including obesity, insulin resistance, and chronic fatigue. They assess how the coenzyme enhances glucose metabolism and improves insulin sensitivity. By improving these processes, NAD+ supports ongoing research into managing metabolic imbalances and promoting energy homeostasis.
Each 1000mg batch undergoes comprehensive testing to ensure high purity and consistency. Researchers depend on this coenzyme to achieve reliable outcomes in studies involving mitochondrial health and cellular metabolism.
Finally, NAD+ continues to drive advancements in research on aging, metabolic health, and energy regulation. Through its critical role in activating key metabolic pathways, it helps scientists develop innovative strategies for enhancing mitochondrial function, reducing cellular stress, and improving overall health.